Increasing the minimum wage would have two principal effects on low-wage
workers. Most of them would receive higher pay that would increase their
familyfs income, and some of those families would see their income rise above
the federal poverty threshold. But some jobs for low-wage workers would probably
be eliminated, the income of most workers who became jobless would fall
substantially, and the share of low-wage workers who were employed would
probably fall slightly.
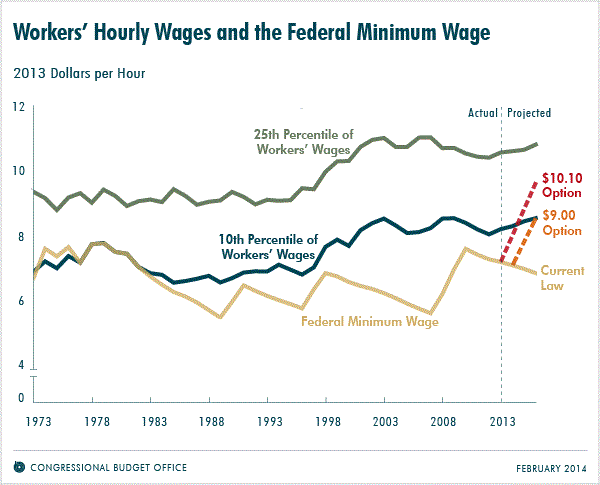
What Options for Increasing the Minimum Wage Did CBO Examine?
For this report, CBO examined the effects on employment and family income of
two options for increasing the federal minimum wage (see the figure below):
- A g$10.10 optionh would increase the federal minimum wage from its current
rate of $7.25 per hour to $10.10 per hour in three steps—in 2014, 2015, and
2016. After reaching $10.10 in 2016, the minimum wage would be adjusted
annually for inflation as measured by the consumer price index.
- A g$9.00 optionh would raise the federal minimum wage from $7.25 per hour
to $9.00 per hour in two steps—in 2015 and 2016. After reaching $9.00 in 2016,
the minimum wage would not be subsequently adjusted for inflation.
What Effects Would Those Options Have?
The $10.10 option would have substantially larger effects on employment and
income than the $9.00 option would—because more workers would see their wages
rise; the change in their wages would be greater; and, CBO expects, employment
would be more responsive to a minimum-wage increase that was larger and was
subsequently adjusted for inflation. The net effect of either option on the
federal budget would probably be small.
Effects of the $10.10 Option on Employment and Income
Once fully implemented in the second half of 2016, the $10.10 option would
reduce total employment by about 500,000 workers, or 0.3 percent, CBO projects
(see the table below). As with any such estimates, however, the actual losses
could be smaller or larger; in CBOfs assessment, there is about a two-thirds
chance that the effect would be in the range between a very slight reduction in
employment and a reduction in employment of 1.0 million workers.

Many more low-wage workers would see an increase in their earnings. Of those
workers who will earn up to $10.10 under current law, most—about 16.5 million,
according to CBOfs estimates—would have higher earnings during an average week
in the second half of 2016 if the $10.10 option was implemented. Some of the
people earning slightly more than $10.10 would also have higher earnings under
that option, for reasons discussed below. Further, a few higher-wage workers
would owe their jobs and increased earnings to the heightened demand for goods
and services that would result from the minimum-wage increase.
The increased earnings for low-wage workers resulting from the higher minimum
wage would total $31 billion, by CBOfs estimate. However, those earnings would
not go only to low-income families, because many low-wage workers are not
members of low-income families. Just 19 percent of the $31 billion would accrue
to families with earnings below the poverty threshold, whereas 29 percent would
accrue to families earning more than three times the poverty threshold, CBO
estimates.
Moreover, the increased earnings for some workers would be accompanied by
reductions in real (inflation-adjusted) income for the people who became jobless
because of the minimum-wage increase, for business owners, and for consumers
facing higher prices. CBO examined family income overall and for various income
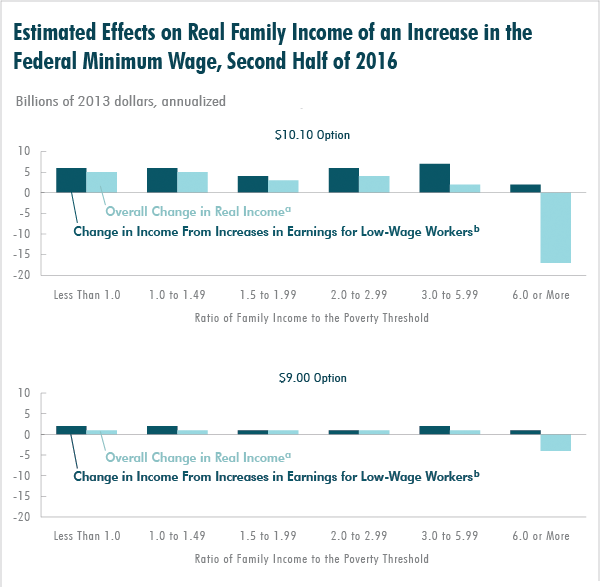
groups, reaching the following conclusions (see the figure below):
- Once the increases and decreases in income for all workers are taken into
account, overall real income would rise by $2 billion.
- Real income would increase, on net, by $5 billion for families whose
income will be below the poverty threshold under current law, boosting their
average family income by about 3 percent and moving about 900,000 people, on
net, above the poverty threshold (out of the roughly 45 million people who are
projected to be below that threshold under current law).
- Families whose income would have been between one and three times the
poverty threshold would receive, on net, $12 billion in additional real
income. About $2 billion, on net, would go to families whose income would have
been between three and six times the poverty threshold.
- Real income would decrease, on net, by $17 billion for families whose
income would otherwise have been six times the poverty threshold or more,
lowering their average family income by 0.4 percent.
Effects of the $9.00 Option on Employment and Income
The $9.00 option would reduce employment by about 100,000 workers, or by less
than 0.1 percent, CBO projects. There is about a two-thirds chance that the
effect would be in the range between a very slight increase in employment and a
reduction in employment of 200,000 workers, in CBOfs assessment. Roughly 7.6
million workers who will earn up to $9.00 per hour under current law would have
higher earnings during an average week in the second half of 2016 if this option
was implemented, CBO estimates, and some people earning more than $9.00 would
have higher earnings as well.
The increased earnings for low-wage workers resulting from the higher minimum
wage would total $9 billion; 22 percent of that sum would accrue to families
with income below the poverty threshold, whereas 33 percent would accrue to
families earning more than three times the poverty threshold, CBO estimates.
For family income overall and for various income groups, CBO estimates the
following:
- Once the increases and decreases in income for all workers are taken into
account, overall real income would rise by $1 billion.
- Real income would increase, on net, by about $1 billion for families whose
income will be below the poverty threshold under current law, boosting their
average family income by about 1 percent and moving about 300,000 people, on
net, above the poverty threshold.
- Families whose income would have been between one and three times the
poverty threshold would receive, on net, $3 billion in additional real income.
About $1 billion, on net, would go to families whose income would have been
between three and six times the poverty threshold.
- Real income would decrease, on net, by $4 billion for families whose
income would otherwise have been six times the poverty threshold or more,
lowering their average family income by about 0.1 percent.
Effects of a Minimum-Wage Increase on the Federal Budget
In addition to affecting employment and family income, increasing the federal
minimum wage would affect the federal budget directly by increasing the wages
that the federal government paid to a small number of hourly employees and
indirectly by boosting the prices of some goods and services purchased by the
government. Most of those costs would need to be covered by discretionary
appropriations, which are capped through 2021 under current law.
Federal spending and taxes would also be indirectly affected by the increases
in real income for some people and the reduction in real income for others. As a
group, workers with increased earnings would pay more in taxes and receive less
in federal benefits of certain types than they would have otherwise. However,
people who became jobless because of the minimum-wage increase, business owners,
and consumers facing higher prices would see a reduction in real income and
would collectively pay less in taxes and receive more in federal benefits than
they would have otherwise. CBO concludes that the net effect on the federal
budget of raising the minimum wage would probably be a small decrease in budget
deficits for several years but a small increase in budget deficits thereafter.
It is unclear whether the effect for the coming decade as a whole would be a
small increase or a small decrease in budget deficits.